# 实现链路控制
# 实验介绍
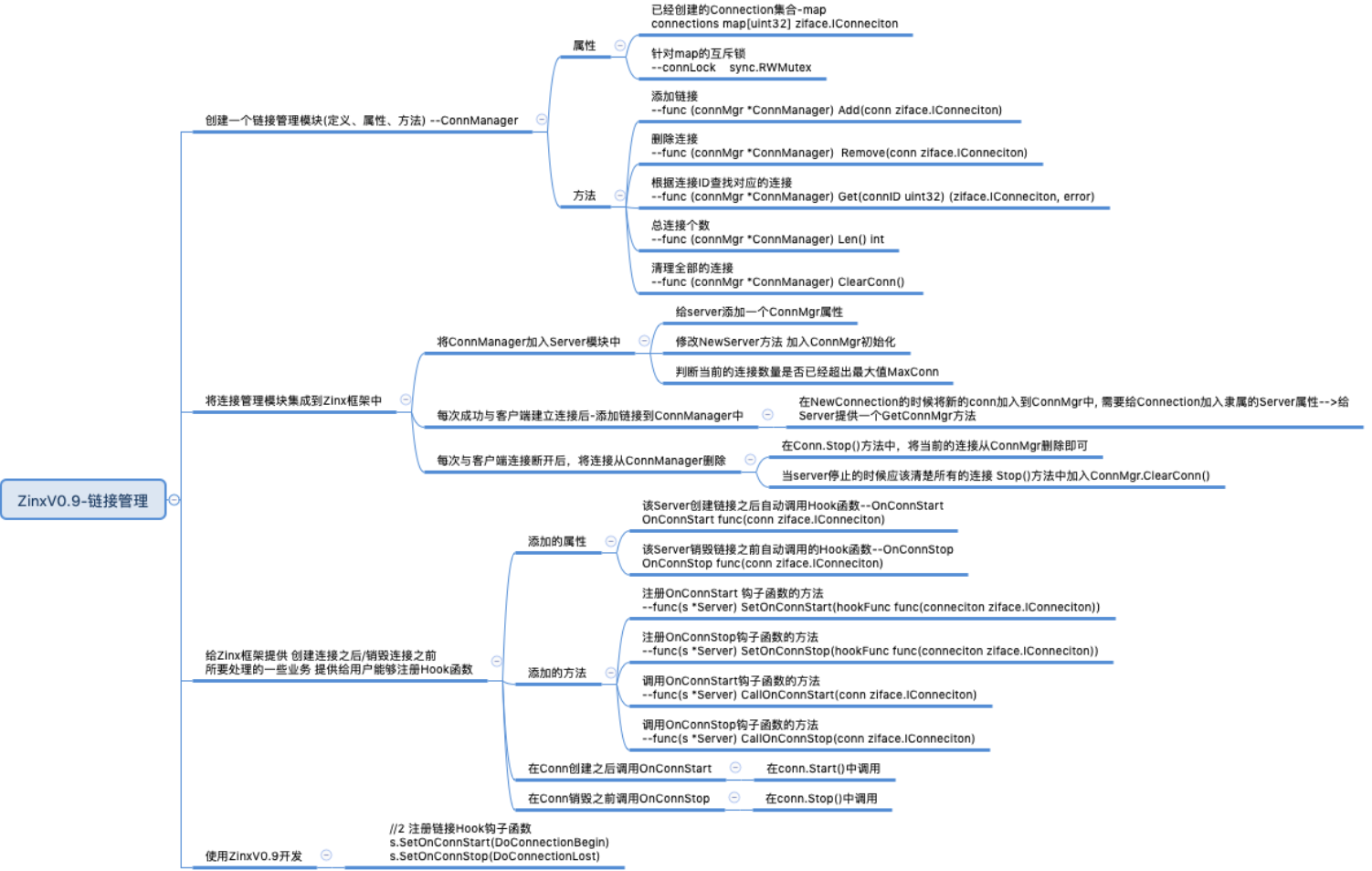
我们现在就需要给 Zinx 添加链接管理机制了。 本节思维导图比较大,建议同学们右键保存到本地放大查看。
# 准备工作
我们先在命令行中执行如下代码:
wget https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1639/src08.zip && unzip src08.zip
export GOPATH=/home/project
2
执行后我们的项目目录如下:
之前我们已经实现了让 zinx 可以处理多链接请求,现在我们要为 Zinx 框架增加链接个数的限定,如果超过一定量的客户端个数,Zinx 为了保证后端的及时响应,而拒绝链接请求。
# 创建链接管理模块
这里面我们就需要对链接有一个管理的模块。
我们在 ziface 和 znet 分别建立 iconnmanager.go 和 connmanager.go 文件。
zinx/ziface/iconmanager.go
package ziface
/*
连接管理抽象层
*/
type IConnManager interface {
Add(conn IConnection) //添加链接
Remove(conn IConnection) //删除连接
Get(connID uint32) (IConnection, error) //利用ConnID获取链接
Len() int //获取当前连接
ClearConn() //删除并停止所有链接
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
这里定义了一些接口方法,添加链接、删除链接、根据 ID 获取链接、链接数量、和清除链接等。下面我们对这个接口进行实现。
zinx/znet/connmanager.go
这里面 ConnManager 中,其中用一个 map 来承载全部的连接信息,key 是连接 ID,value 则是连接本身。其中有一个读写锁 connLock 主要是针对 map 做多任务修改时的保护作用。
Remove() 方法只是单纯的将 conn 从 map 中摘掉,而 ClearConn() 方法则会先停止链接业务,c.Stop(),然后再从 map 中摘除。
package znet
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"sync"
"zinx/ziface"
)
/*
连接管理模块
*/
type ConnManager struct {
connections map[uint32]ziface.IConnection //管理的连接信息
connLock sync.RWMutex //读写连接的读写锁
}
/*
创建一个链接管理
*/
func NewConnManager() *ConnManager {
return &ConnManager{
connections:make(map[uint32] ziface.IConnection),
}
}
//添加链接
func (connMgr *ConnManager) Add(conn ziface.IConnection) {
//保护共享资源Map 加写锁
connMgr.connLock.Lock()
defer connMgr.connLock.Unlock()
//将conn连接添加到ConnMananger中
connMgr.connections[conn.GetConnID()] = conn
fmt.Println("connection add to ConnManager successfully: conn num = ", connMgr.Len())
}
//删除连接
func (connMgr *ConnManager) Remove(conn ziface.IConnection) {
//保护共享资源Map 加写锁
connMgr.connLock.Lock()
defer connMgr.connLock.Unlock()
//删除连接信息
delete(connMgr.connections, conn.GetConnID())
fmt.Println("connection Remove ConnID=",conn.GetConnID(), " successfully: conn num = ", connMgr.Len())
}
//利用ConnID获取链接
func (connMgr *ConnManager) Get(connID uint32) (ziface.IConnection, error) {
//保护共享资源Map 加读锁
connMgr.connLock.RLock()
defer connMgr.connLock.RUnlock()
if conn, ok := connMgr.connections[connID]; ok {
return conn, nil
} else {
return nil, errors.New("connection not found")
}
}
//获取当前连接
func (connMgr *ConnManager) Len() int {
return len(connMgr.connections)
}
//清除并停止所有连接
func (connMgr *ConnManager) ClearConn() {
//保护共享资源Map 加写锁
connMgr.connLock.Lock()
defer connMgr.connLock.Unlock()
//停止并删除全部的连接信息
for connID, conn := range connMgr.connections {
//停止
conn.Stop()
//删除
delete(connMgr.connections,connID)
}
fmt.Println("Clear All Connections successfully: conn num = ", connMgr.Len())
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
# 链接管理模块集成到 Zinx 中
现在需要将ConnManager添加到Server中。
zinx/znet/server.go
//iServer 接口实现,定义一个Server服务类
type Server struct {
//服务器的名称
Name string
//tcp4 or other
IPVersion string
//服务绑定的IP地址
IP string
//服务绑定的端口
Port int
//当前Server的消息管理模块,用来绑定MsgId和对应的处理方法
msgHandler ziface.IMsgHandle
//当前Server的链接管理器
ConnMgr ziface.IConnManager
}
/*
创建一个服务器句柄
*/
func NewServer () ziface.IServer {
utils.GlobalObject.Reload()
s:= &Server {
Name :utils.GlobalObject.Name,
IPVersion:"tcp4",
IP:utils.GlobalObject.Host,
Port:utils.GlobalObject.TcpPort,
msgHandler: NewMsgHandle(),
ConnMgr:NewConnManager(), //创建ConnManager
}
return s
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
现在,既然 server 具备了 ConnManager 成员,在获取的时候需要给抽象层提供一个获取 ConnManager 方法 。
zinx/ziface/iserver.go
type IServer interface{
//启动服务器方法
Start()
//停止服务器方法
Stop()
//开启业务服务方法
Serve()
//路由功能:给当前服务注册一个路由业务方法,供客户端链接处理使用
AddRouter(msgId uint32, router IRouter)
//得到链接管理
GetConnMgr() IConnManager
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
zinx/znet/server.go
//得到链接管理
func (s *Server) GetConnMgr() ziface.IConnManager {
return s.ConnMgr
}
2
3
4
因为我们现在在 server 中有链接的管理,有的时候 conn 也需要得到这个 ConnMgr 的使用权,那么我们需要将Server和Connection建立能够互相索引的关系,我们在Connection中,添加 Server 当前 conn 隶属的 server 句柄。
zinx/znet/connection.go
type Connection struct {
//当前Conn属于哪个Server
TcpServer ziface.IServer //当前conn属于哪个server,在conn初始化的时候添加即可
//当前连接的socket TCP套接字
Conn *net.TCPConn
//当前连接的ID 也可以称作为SessionID,ID全局唯一
ConnID uint32
//当前连接的关闭状态
isClosed bool
//消息管理MsgId和对应处理方法的消息管理模块
MsgHandler ziface.IMsgHandle
//告知该链接已经退出/停止的channel
ExitBuffChan chan bool
//无缓冲管道,用于读、写两个goroutine之间的消息通信
msgChan chan []byte
//有关冲管道,用于读、写两个goroutine之间的消息通信
msgBuffChan chan []byte
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 链接的添加
现在我们怎么样选择将创建好的连接添加到ConnManager中呢,这里我们选择在初始化一个新链接的时候,加进来就好了。
zinx/znet/connection.go
//创建连接的方法
func NewConntion(server ziface.IServer, conn *net.TCPConn, connID uint32, msgHandler ziface.IMsgHandle) *Connection{
//初始化Conn属性
c := &Connection{
TcpServer:server, //将隶属的server传递进来
Conn: conn,
ConnID: connID,
isClosed: false,
MsgHandler: msgHandler,
ExitBuffChan: make(chan bool, 1),
msgChan:make(chan []byte),
msgBuffChan:make(chan []byte, utils.GlobalObject.MaxMsgChanLen),
}
//将新创建的Conn添加到链接管理中
c.TcpServer.GetConnMgr().Add(c) //将当前新创建的连接添加到ConnManager中
return c
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# Server 中添加链接数量的判断
在 server 的Start()方法中,在 Accept 与客户端链接建立成功后,可以直接对链接的个数做一个判断。
zinx/znet/server.go
//开启网络服务
// 注意 // ... 的部分是对应的原来的代码不需要变动
func (s *Server) Start() {
fmt.Printf("[START] Server name: %s,listenner at IP: %s, Port %d is starting\n", s.Name, s.IP, s.Port)
fmt.Printf("[Zinx] Version: %s, MaxConn: %d, MaxPacketSize: %d\n",
utils.GlobalObject.Version,
utils.GlobalObject.MaxConn,
utils.GlobalObject.MaxPacketSize)
//开启一个go去做服务端Linster业务
go func() {
// ....
//3 启动server网络连接业务
for {
//3.1 阻塞等待客户端建立连接请求
conn, err := listenner.AcceptTCP()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Accept err ", err)
continue
}
//=============
//3.2 设置服务器最大连接控制,如果超过最大连接,那么则关闭此新的连接
if s.ConnMgr.Len() >= utils.GlobalObject.MaxConn {
conn.Close()
continue
}
//=============
//3.3 处理该新连接请求的 业务 方法, 此时应该有 handler 和 conn是绑定的
dealConn := NewConntion(s, conn, cid, s.msgHandler)
cid ++
//3.4 启动当前链接的处理业务
go dealConn.Start()
}
}()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
当然,我们应该在配置文件zinx.json或者在GlobalObject全局配置中,定义好我们期望的连接的最大数目限制MaxConn。 同时,因为这里添加了一个新的属性,所以全局配置也需要做出修改:
zinx/utils/globalobj.go
type GlobalObj struct {
/*
Server
*/
TcpServer ziface.IServer //当前Zinx的全局Server对象
Host string //当前服务器主机IP
TcpPort int //当前服务器主机监听端口号
Name string //当前服务器名称
/*
Zinx
*/
Version string //当前Zinx版本号
MaxPacketSize uint32 //都需数据包的最大值
MaxConn int //当前服务器主机允许的最大链接个数
WorkerPoolSize uint32 //业务工作Worker池的数量
MaxWorkerTaskLen uint32 //业务工作Worker对应负责的任务队列最大任务存储数量
MaxMsgChanLen int
/*
config file path
*/
ConfFilePath string
}
/*
提供init方法,默认加载
*/
func init() {
//初始化GlobalObject变量,设置一些默认值
GlobalObject = &GlobalObj{
Name: "ZinxServerApp",
Version: "V0.4",
TcpPort: 7777,
Host: "0.0.0.0",
MaxConn: 12000,
MaxPacketSize: 4096,
ConfFilePath: "conf/zinx.json",
WorkerPoolSize: 10,
MaxWorkerTaskLen: 1024,
MaxMsgChanLen: 16,
}
//从配置文件中加载一些用户配置的参数
GlobalObject.Reload()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# 连接的删除
我们应该在连接停止的时候,将该连接从 ConnManager 中删除,所以在connection的Stop()方法中添加。
zinx/znet/connecion.go
func (c *Connection) Stop() {
fmt.Println("Conn Stop()...ConnID = ", c.ConnID)
//如果当前链接已经关闭
if c.isClosed == true {
return
}
c.isClosed = true
// 关闭socket链接
c.Conn.Close()
//关闭Writer Goroutine
c.ExitBuffChan <- true
//将链接从连接管理器中删除
c.TcpServer.GetConnMgr().Remove(c) //删除conn从ConnManager中
//关闭该链接全部管道
close(c.ExitBuffChan)
close(c.msgBuffChan)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
当然,我们也应该在server停止的时候,将全部的连接清空。
zinx/znet/server.go
func (s *Server) Stop() {
fmt.Println("[STOP] Zinx server , name " , s.Name)
//将其他需要清理的连接信息或者其他信息 也要一并停止或者清理
s.ConnMgr.ClearConn()
}
2
3
4
5
现在我们已经将连接管理成功的集成到了 Zinx 之中了。 下面我们接着实现带缓冲的发包方法。
# 链接的带缓冲的发包方法
我们之前给Connection提供了一个发消息的方法SendMsg(),这个是将数据发送到一个无缓冲的 channel 中msgChan。但是如果客户端链接比较多的话,如果对方处理不及时,可能会出现短暂的阻塞现象,我们可以做一个提供一定缓冲的发消息方法,做一些非阻塞的发送体验。
zinx/ziface/iconnection.go
//定义连接接口
type IConnection interface {
//启动连接,让当前连接开始工作
Start()
//停止连接,结束当前连接状态M
Stop()
//从当前连接获取原始的socket TCPConn
GetTCPConnection() *net.TCPConn
//获取当前连接ID
GetConnID() uint32
//获取远程客户端地址信息
RemoteAddr() net.Addr
//直接将Message数据发送数据给远程的TCP客户端(无缓冲)
SendMsg(msgId uint32, data []byte) error
//直接将Message数据发送给远程的TCP客户端(有缓冲)
SendBuffMsg(msgId uint32, data []byte) error //添加带缓冲发送消息接口
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
zinx/znet/connection.go
type Connection struct {
//当前Conn属于哪个Server
TcpServer ziface.IServer
//当前连接的socket TCP套接字
Conn *net.TCPConn
//当前连接的ID 也可以称作为SessionID,ID全局唯一
ConnID uint32
//当前连接的关闭状态
isClosed bool
//消息管理MsgId和对应处理方法的消息管理模块
MsgHandler ziface.IMsgHandle
//告知该链接已经退出/停止的channel
ExitBuffChan chan bool
//无缓冲管道,用于读、写两个goroutine之间的消息通信
msgChan chan []byte
//有关冲管道,用于读、写两个goroutine之间的消息通信
msgBuffChan chan []byte //定义channel成员
}
//创建连接的方法
func NewConntion(server ziface.IServer, conn *net.TCPConn, connID uint32, msgHandler ziface.IMsgHandle) *Connection{
//初始化Conn属性
c := &Connection{
TcpServer:server,
Conn: conn,
ConnID: connID,
isClosed: false,
MsgHandler: msgHandler,
ExitBuffChan: make(chan bool, 1),
msgChan:make(chan []byte),
msgBuffChan:make(chan []byte, utils.GlobalObject.MaxMsgChanLen), //不要忘记初始化
}
//将新创建的Conn添加到链接管理中
c.TcpServer.GetConnMgr().Add(c)
return c
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
然后将SendBuffMsg()方法实现一下:
func (c *Connection) SendBuffMsg(msgId uint32, data []byte) error {
if c.isClosed == true {
return errors.New("Connection closed when send buff msg")
}
//将data封包,并且发送
dp := NewDataPack()
msg, err := dp.Pack(NewMsgPackage(msgId, data))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Pack error msg id = ", msgId)
return errors.New("Pack error msg ")
}
//写回客户端
c.msgBuffChan <- msg
return nil
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
我们在 Writer 中也要有对msgBuffChan的数据监控:
/*
写消息Goroutine, 用户将数据发送给客户端
*/
func (c *Connection) StartWriter() {
fmt.Println("[Writer Goroutine is running]")
defer fmt.Println(c.RemoteAddr().String(), "[conn Writer exit!]")
for {
select {
case data := <-c.msgChan:
//有数据要写给客户端
if _, err := c.Conn.Write(data); err != nil {
fmt.Println("Send Data error:, ", err, " Conn Writer exit")
return
}
//针对有缓冲channel需要些的数据处理
case data, ok:= <-c.msgBuffChan:
if ok {
//有数据要写给客户端
if _, err := c.Conn.Write(data); err != nil {
fmt.Println("Send Buff Data error:, ", err, " Conn Writer exit")
return
}
} else {
break
fmt.Println("msgBuffChan is Closed")
}
case <-c.ExitBuffChan:
return
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
现在,我们实现了带缓冲的发包方法。接下来,我们去实现注册链接启动/停止自定义 Hook 方法功能。
# 注册链接启动/停止自定义 Hook 方法功能
有的时候,在创建链接的时候,希望在创建链接之后、和断开链接之前,执行一些用户自定义的业务。那么我们就需要给 Zinx 增添两个链接创建后和断开前时机的回调函数,一般也称作 Hook(钩子)函数。
我们可以通过 Server 来注册 conn 的 hook 方法
zinx/ziface/iserver.go
type IServer interface{
//启动服务器方法
Start()
//停止服务器方法
Stop()
//开启业务服务方法
Serve()
//路由功能:给当前服务注册一个路由业务方法,供客户端链接处理使用
AddRouter(msgId uint32, router IRouter)
//得到链接管理
GetConnMgr() IConnManager
//设置该Server的连接创建时Hook函数
SetOnConnStart(func (IConnection))
//设置该Server的连接断开时的Hook函数
SetOnConnStop(func (IConnection))
//调用连接OnConnStart Hook函数
CallOnConnStart(conn IConnection)
//调用连接OnConnStop Hook函数
CallOnConnStop(conn IConnection)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
zinx/znet/server.go
//iServer 接口实现,定义一个Server服务类
type Server struct {
//服务器的名称
Name string
//tcp4 or other
IPVersion string
//服务绑定的IP地址
IP string
//服务绑定的端口
Port int
//当前Server的消息管理模块,用来绑定MsgId和对应的处理方法
msgHandler ziface.IMsgHandle
//当前Server的链接管理器
ConnMgr ziface.IConnManager
// =======================
//新增两个hook函数原型
//该Server的连接创建时Hook函数
OnConnStart func(conn ziface.IConnection)
//该Server的连接断开时的Hook函数
OnConnStop func(conn ziface.IConnection)
// =======================
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
实现添加 hook 函数的接口和调用 hook 函数的接口。
//设置该Server的连接创建时Hook函数
func (s *Server) SetOnConnStart(hookFunc func (ziface.IConnection)) {
s.OnConnStart = hookFunc
}
//设置该Server的连接断开时的Hook函数
func (s *Server) SetOnConnStop(hookFunc func (ziface.IConnection)) {
s.OnConnStop = hookFunc
}
//调用连接OnConnStart Hook函数
func (s *Server) CallOnConnStart(conn ziface.IConnection) {
if s.OnConnStart != nil {
fmt.Println("---> CallOnConnStart....")
s.OnConnStart(conn)
}
}
//调用连接OnConnStop Hook函数
func (s *Server) CallOnConnStop(conn ziface.IConnection) {
if s.OnConnStop != nil {
fmt.Println("---> CallOnConnStop....")
s.OnConnStop(conn)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
那么接下来,需要选定两个 Hook 方法的调用位置。
一个是创建链接之后:
zinx/znet/connection.go
//启动连接,让当前连接开始工作
func (c *Connection) Start() {
//1 开启用户从客户端读取数据流程的Goroutine
go c.StartReader()
//2 开启用于写回客户端数据流程的Goroutine
go c.StartWriter()
//==================
//按照用户传递进来的创建连接时需要处理的业务,执行钩子方法
c.TcpServer.CallOnConnStart(c)
//==================
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
一个是停止链接之前:
zinx/znet/connection.go
//停止连接,结束当前连接状态M
func (c *Connection) Stop() {
fmt.Println("Conn Stop()...ConnID = ", c.ConnID)
//如果当前链接已经关闭
if c.isClosed == true {
return
}
c.isClosed = true
//==================
//如果用户注册了该链接的关闭回调业务,那么在此刻应该显示调用
c.TcpServer.CallOnConnStop(c)
//==================
// 关闭socket链接
c.Conn.Close()
//关闭Writer
c.ExitBuffChan <- true
//将链接从连接管理器中删除
c.TcpServer.GetConnMgr().Remove(c)
//关闭该链接全部管道
close(c.ExitBuffChan)
close(c.msgBuffChan)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
好了,现在我们基本上已经将全部的连接管理的功能集成到 Zinx 中了,接下来就需要测试一下链接管理模块是否可以使用了。
# 测试
写一个服务端:
Server.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"zinx/ziface"
"zinx/znet"
)
//ping test 自定义路由
type PingRouter struct {
znet.BaseRouter
}
//Ping Handle
func (this *PingRouter) Handle(request ziface.IRequest) {
fmt.Println("Call PingRouter Handle")
//先读取客户端的数据,再回写ping...ping...ping
fmt.Println("recv from client : msgId=", request.GetMsgID(), ", data=", string(request.GetData()))
err := request.GetConnection().SendBuffMsg(0, []byte("ping...ping...ping"))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
type HelloZinxRouter struct {
znet.BaseRouter
}
//HelloZinxRouter Handle
func (this *HelloZinxRouter) Handle(request ziface.IRequest) {
fmt.Println("Call HelloZinxRouter Handle")
//先读取客户端的数据,再回写ping...ping...ping
fmt.Println("recv from client : msgId=", request.GetMsgID(), ", data=", string(request.GetData()))
err := request.GetConnection().SendBuffMsg(1, []byte("Hello Zinx Router V0.8"))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
//创建连接的时候执行
func DoConnectionBegin(conn ziface.IConnection) {
fmt.Println("DoConnecionBegin is Called ... ")
err := conn.SendMsg(2, []byte("DoConnection BEGIN..."))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
//连接断开的时候执行
func DoConnectionLost(conn ziface.IConnection) {
fmt.Println("DoConneciotnLost is Called ... ")
}
func main() {
//创建一个server句柄
s := znet.NewServer()
//注册链接hook回调函数
s.SetOnConnStart(DoConnectionBegin)
s.SetOnConnStop(DoConnectionLost)
//配置路由
s.AddRouter(0, &PingRouter{})
s.AddRouter(1, &HelloZinxRouter{})
//开启服务
s.Serve()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
我们这里注册了两个 Hook 函数一个是链接初始化之后DoConnectionBegin()和链接停止之前DoConnectionLost()。
DoConnectionBegin()会发给客户端一个消息 2 的文本,并且在服务端打印一个调试信息"DoConnecionBegin is Called..."
DoConnectionLost()在服务端打印一个调试信息"DoConneciotnLost is Called..."
客户端:
Client.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"net"
"time"
"zinx/znet"
)
/*
模拟客户端
*/
func main() {
fmt.Println("Client Test ... start")
//3秒之后发起测试请求,给服务端开启服务的机会
time.Sleep(3 * time.Second)
conn,err := net.Dial("tcp", "127.0.0.1:7777")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("client start err, exit!")
return
}
for {
//发封包message消息
dp := znet.NewDataPack()
msg, _ := dp.Pack(znet.NewMsgPackage(0,[]byte("Zinx V0.8 Client0 Test Message")))
_, err := conn.Write(msg)
if err !=nil {
fmt.Println("write error err ", err)
return
}
//先读出流中的head部分
headData := make([]byte, dp.GetHeadLen())
_, err = io.ReadFull(conn, headData) //ReadFull 会把msg填充满为止
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("read head error")
break
}
//将headData字节流 拆包到msg中
msgHead, err := dp.Unpack(headData)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("server unpack err:", err)
return
}
if msgHead.GetDataLen() > 0 {
//msg 是有data数据的,需要再次读取data数据
msg := msgHead.(*znet.Message)
msg.Data = make([]byte, msg.GetDataLen())
//根据dataLen从io中读取字节流
_, err := io.ReadFull(conn, msg.Data)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("server unpack data err:", err)
return
}
fmt.Println("==> Recv Msg: ID=", msg.Id, ", len=", msg.DataLen, ", data=", string(msg.Data))
}
time.Sleep(1*time.Second)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
我们在当前命令行窗口启动服务端:
go run Server.go
之后新建另一个命令行窗口,即命令行右上角的按钮。点击后先在新的命令行窗口输入 export GOPATH=/home/project 再切换到 zinx 目录下执行 go run Client.go。
测试结果:
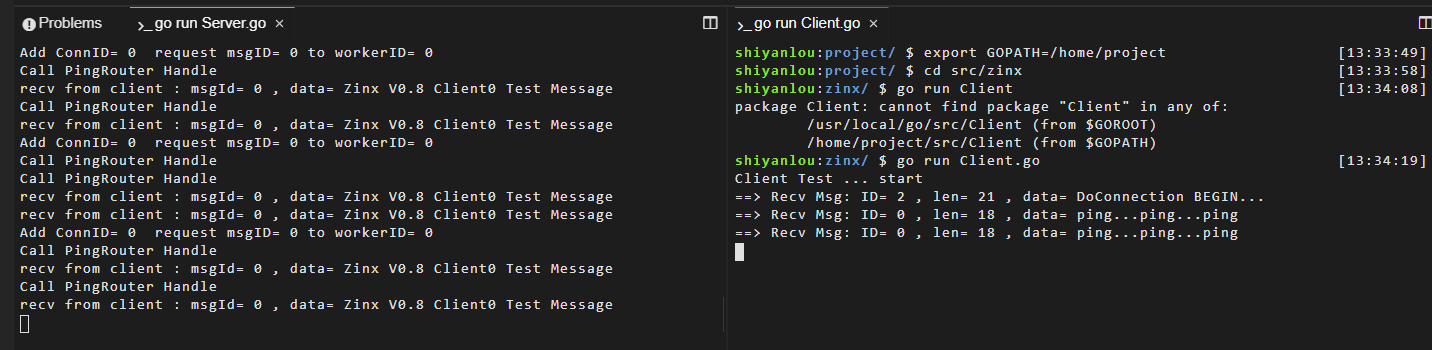
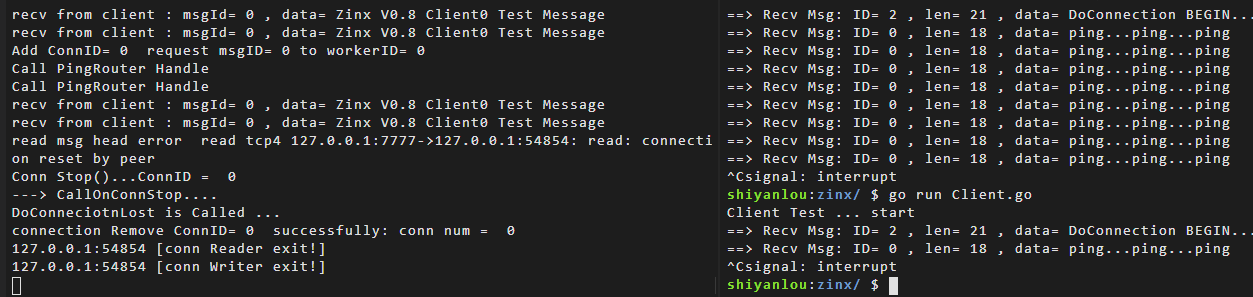
客户端创建成功,回调 Hook 已经执行,并且 Conn 被添加到 ConnManager 中, conn num = 1,当我们手动 CTRL+C 关闭客户端的时候, 服务器 ConnManager 已经成功将 Conn 摘掉,conn num = 0。
同时服务端也打印出 conn 停止之后的回调信息。
# 实验总结
今天我们完成了 zinx 0.9 版本,完成了链接控制的功能,以及缓冲包的使用,大家在实验结束后请思考一下,使用缓冲和不使用缓冲的优缺点是什么。