# 计算属性和侦听属性与过滤器
# 计算属性
在开发中经常会涉及到一种需求,一个数据需要通过其他数据计算而来。例如:购物车,平常开发数据与数据关联计算是非常麻烦的,而 Vue 中的计算属性可以轻松帮你解决,可以像绑定普通属性一样在模板中绑定计算属性,可以直接使用{{}}向页面输出。
# 计算属性的基本使用
在实例的 computed 选项中定义你的计算属性,直接使用{{}}向页面输出。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>我名字正着写:{{name}}</p>
<!-- reverseName 计算属性 可以像绑定普通属性一样在模板中绑定计算属性-->
<p>计算出我名字倒着写:{{reverseName}}</p>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "实验楼",
},
computed: {
//reverseName 是一个计算属性
reverseName: function () {
return this.name.split("").reverse().join("");
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
运行结果:
这里我们声明了一个计算属性 reverseName ,你可以像绑定普通属性一样在模板中绑定计算属性。当你的计算属性的依赖数据发生改变时,你的相关计算属性也会重新计算。上面通过计算属性轻松地实现出展示名字倒着写,你也快看看,你名字倒过来是什么!
重点: 在 Vue 中计算属性是 惰性的,只有当依赖数据发生改变时,才会触发计算,否则,它的值是上一次触发计算的缓存值,下面例子很清楚说明,它是惰性的。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">{{now}}</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {},
computed: {
now: function () {
return Date.now();
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
在你的理解中界面会一直时间更新,其实我们定义的 now 并没有和实例中数据建立响应式依赖,只是依赖 Date 对象获取系统时间,它只会计算一次,然后将值缓存,要使得他改变只有 刷新 才能触发,运行结果:

# 计算属性的 setter 和 getter
计算属性的 setter 和 getter 是它的高级使用,上面的例子只使用到它的 getter 属性,通过其他数据计算而得,其实我们也可以,直接赋值,通过计算属性来改变依赖数据的值。
下面例子我们通过触发计算属性 setter,改变原本关联数据。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>firstName:{{firstName}}</p>
<p>lastName:{{lastName}}</p>
<p>全名是:{{fullName}}</p>
<button v-on:click="changeName">改姓</button>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
firstName: "王",
lastName: "花花",
},
methods: {
//changeName 定义一个方法改变 计算属性 fullName 的值
changeName: function () {
//修改计算属性 fullName 等于李花花
this.fullName = "李花花";
//上面一句等于触发了 fullName 属性的 setter
},
},
computed: {
fullName: {
//getter
get: function () {
return this.firstName + this.lastName;
},
//setter 直接改变计算属性 fullName的值就可以触发setter this.fullName='XX'
set: function (newName) {
var name = newName;
this.firstName = name.slice(0, 1); //取新值的第一个字符
this.lastName = name.slice(1); //从新值的第二个字符开始取值
},
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
运行结果:

# 侦听属性
在开发我们需要监听数据的变化,Vue 提供了一种更通用的方式来观察和响应 Vue 实例上的数据变动,侦听属性。在实例 watch 选项中确定监听项。
下面这个例子,我们通过按钮点击改变 msg 的值,并且监听新旧值改变,并输出新旧值。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{msg}}</p>
<!-- v-on:click 简写为 @click -->
<button @click="handleClick('hello syl')">改变msg</button>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
msg: "hello",
},
methods: {
//改变 msg的值
handleClick: function (val) {
this.msg = val;
},
},
// watch 监听属性
watch: {
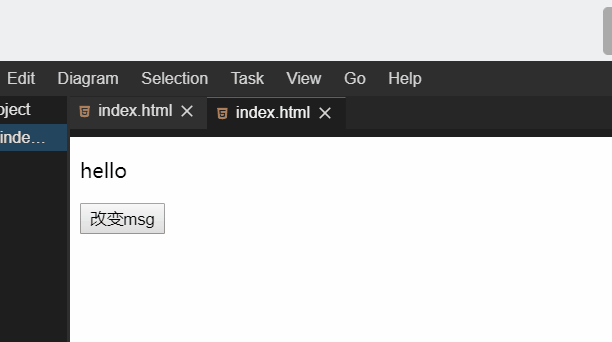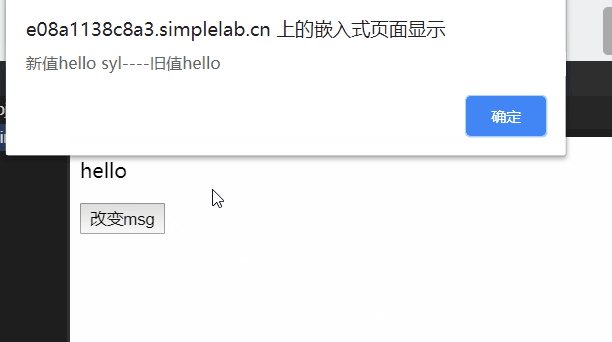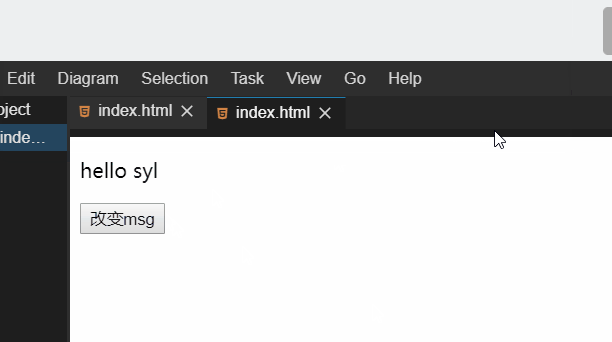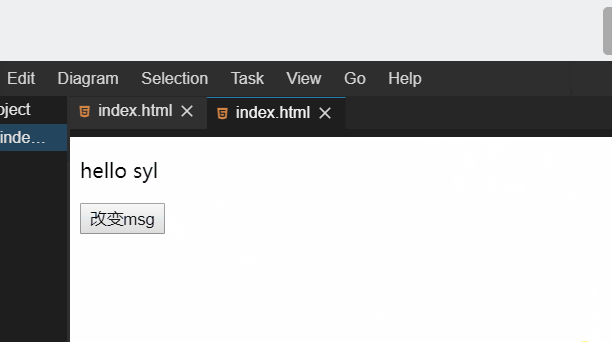
//监听新旧值 监听属性有两个参数,第一个新值,第二个旧值
msg: function (newVal, oldVal) {
alert("新值" + newVal + "----" + "旧值" + oldVal);
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
运行效果:
# 计算属性与侦听属性对比
计算属性和侦听属性两者在很多场景都是共同,都可以实现同样的需求。
我们使用侦听属性,改写计算属性例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>firstName:{{firstName}}</p>
<p>lastName:{{lastName}}</p>
<p>全名是:{{fullName}}</p>
<button v-on:click="changeName">改姓</button>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
firstName: "王",
lastName: "花花",
fullName: "王花花",
},
methods: {
//changeName 定义一个方法改变 fullName 的值
changeName: function () {
this.fullName = "李花花";
},
},
watch: {
//fullName 侦听属性,监听fullName 值的改变
fullName: function (val) {
var name = val;
this.firstName = name.slice(0, 1);
this.lastName = name.slice(1);
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
效果是一样的,运行效果:

注意: 通常来说能用计算属性代替就用计算属性代替,多大情况计算属性代码更精简,可读性更高。
# 过滤器
计算属性和侦听属性,在数据处理环节中很有作用,但是用它来处理数据过滤不是最优的,在 Vue 中我们有一个专门处理数据过滤的东西:过滤器。过滤器可以用在两个地方:双花括号插值和 v-bind 表达式 (后者从 2.1.0+ 开始支持),用法示例:
<p>{{msg2|getString}}</p>
<p v-bind:class="msg2|getString"></p>
2
# 过滤器使用方法
在双花括号插值和 v-bind 表达式中把需要过滤的数据用 | 与过滤器分割 (data|fliter)
例子:
使用 filters 过滤器实现大写转换和自动去除字符串中的数字
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- toUpperCase getString 为自定义的过滤器-->
<p>小写转换大写:过滤前:{{msg}} 过滤后: {{msg|toUpperCase}}</p>
<p>去除数字:过滤前:{{msg2}} 过滤后: {{msg2|getString}}</p>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
msg: "hello",
msg2: "1s2y3l",
},
// filters 过滤器选项
filters: {
//toUpperCase 定义一个字符串转大写的过滤器
toUpperCase: function (val) {
return val.toUpperCase();
},
//getString 定义一个获取去除数字的过滤器
getString: function (val) {
let newVal = "";
val.split("").map(function (item) {
if (9 >= item && item >= 0) {
return;
} else {
return (newVal += item);
}
});
return newVal;
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
运行结果:
# 过滤器应用场景
应用比较多的商品价格过滤、表单数据过滤等。
我们从后台获取的数据一般是这样
{ courseName:'xxx', price:199, coupon:8 }
我们请求到的数据并没有¥,在开发中直接去操作数据源是不推荐的,此时我们的过滤器就派上用场,定义一个拼接¥的过滤器,只是在视图层面实现了效果。

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- joint 为自定义的过滤器-->
<p>不要¥899,只要{{price|joint}}</p>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
//后台价格数据
price: 199,
},
// filters 过滤器选项
filters: {
//joint 定义¥拼接过滤器
joint: function (price) {
return "¥" + price;
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
运行结果:
# 综合小练习
综合计算属性和过滤器,实现一个简易的购物车:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.price {
font-size: 22px;
color: brown;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- joint 为自定义的过滤器-->
<p>单价<span class="price">{{price|joint}}</span></p>
数量:<input type="number" v-model="goodsNum" />
<p>总价:<span class="price">{{allPrice|joint}}</span></p>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
goodsNum: 0,
price: 199,
},
computed: {
allPrice: function () {
return this.goodsNum * this.price;
},
},
// filters 过滤器选项
filters: {
//joint 定义¥拼接过滤器
joint: function (price) {
return "¥" + price;
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
效果:

← 模板语法 class与style绑定 →