# 条件与循环渲染
# 简介
# 条件渲染
# v-if
v-if 指令用于条件性地渲染一块内容。这块内容只会在指令的表达式返回除了 false,0,"",null,undefined 和 NaN 外的值的时候被渲染。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p v-if="display">你好,实验楼</p>
<p>SYL</p>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
display: true,
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
display:true 运行结果:
display:fasle ,运行结果:
# v-else
使用 v-else 指令来表示 v-if 的“else 块”,当 v-if 返回除了 false,0,"",null,undefined 和 NaN 外的值的时候被渲染,否则,就渲染 v-else 块元素。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p v-if="display">你好,实验楼</p>
<p v-else>SYL</p>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
display: true,
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
运行结果:
注意:v-else 元素必须紧跟在带 v-if 或者 v-else-if 的元素的后面,否则它将不会被识别。
# v-show
另一个用于根据条件展示元素的选项是 v-show 指令。不同的是带有 v-show 的元素始终会被渲染并保留在 DOM 中。v-show 只是简单地切换元素的 CSS 属性 display。而 v-if 是从虚拟 DOM 的层面操作。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p v-show="show">你好,实验楼</p>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
show: true,
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
运行结果:
# v-if 和 v-show 比较
一般来说,v-if 会牵涉到虚拟 DOM diff 算法,有更高的切换开销,而 v-show 有更高的初始渲染开销。因此,如果需要非常频繁地切换,则使用 v-show 较好;如果在运行时条件很少改变,则使用 v-if 较好。
我将从以下几点比较 v-if 和 v-show 的区别:
- 渲染方式
v-if会监听对应属性,只有当条件为真的时候才会渲染,当条件为假的时候如已渲染则销毁。v-show一开始便会渲染,通过style控制显示与否。
- 类型
v-if为逻辑运算符,支持v-else、v-else-if等扩展指令,具备有更广泛的数据监听。v-show为比较运算符,通过比较结果来判断该节点是否需要style='display:none'。
- 性能开销
v-if的切换开销大,而v-show在初始渲染时开销最大。因此如果需要非常频繁的切换,使用v-show效果会更好。
# 循环渲染
循环渲染经常会使用到,在开发中经常会遇到 DOM 结构一样的块代码,那么我们就可以使用循环渲染来一步到位。
# v-for 将数组数据渲染成元素
将菜单数组循环成一个完成的菜单:
v-for="(变量,i) in 数组";遍历数组 同时重复生成当前标签,数量和数组中对象的数量一致
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
ul {
width: 100%;
height: 40px;
list-style: none;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
background: yellowgreen;
}
ul li {
width: 20%;
height: 100%;
color: white;
line-height: 40px;
text-align: center;
text-transform: uppercase; //大写转换
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul class="nav">
<li v-for="navItem in nav">{{navItem}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
nav: ["home", "shop", "contact", "about", "name", "mroe", "histroy"],
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
运行结果:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>vue数据的写法</title>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload=function(){
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
address:"北京",
name:"张三",
age:20,
person:{
name:"jack",
age:18,
salary:1100
},
hobby:["唱","跳","rap"],
url:"https://act.codeboy.com/"
}
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>地址:{{address}}</p>
<p>姓名:{{name}}</p>
<p>年龄:{{age}}</p>
<p>爱好:{{hobby}} , 个数:{{hobby.length}}</p>
<p>数组的第一个元素:{{hobby[0]}} </p>
<p>数组的第最后一个元素:{{hobby[2]}} </p>
<!-- 数组的遍历:类似于java里的foreach循环,o表示每次获取到的数据 -->
<p v-for="o in hobby">{{o}}</p>
<!-- o是数据,i是下标 -->
<p v-for="o,i in hobby">下标是:{{i}}---数据是:{{o}}</p>
<p v-for="(o,i) in hobby">下标是:{{i}}---数据是:{{o}}</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# v-for 将对象数据渲染成元素
在开发中我们获取到的数据经常是对象形式
对象数据循环出数据:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-for="val in userInfo">
<p>{{val}}</p>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
userInfo: {
name: "whh",
age: 1,
sex: "woman",
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
运行结果:
# 注意
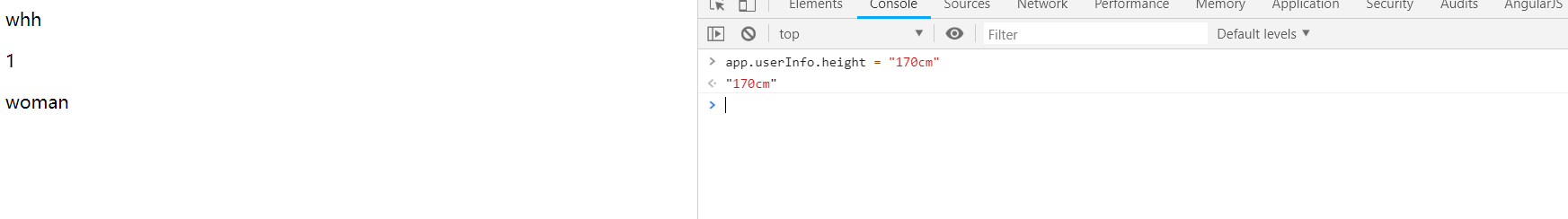
还是由于 JavaScript 的限制,Vue 不能检测对象属性的添加或删除,直接进行 app.userInfo.height='180cm' 这样操作是不会构成响应式,不会触发视图更新。必须使用 Vue.set(object, key, value) 方法向嵌套对象添加响应式属性
直接进行 app.userInfo.height='170cm' ,视图未能更新:
使用 Vue.set(object, key, value) 方法:
Vue.set(app.userInfo, "height", "170cm");
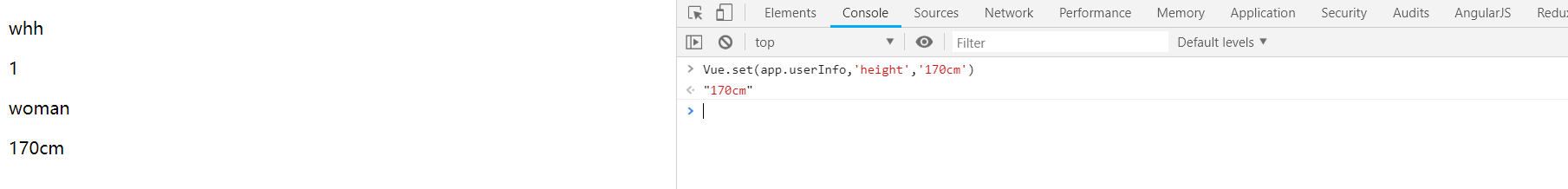
所以,使用对象方法时,要想触发视图更新,常常需要使用 Vue.set()去操作。
# key 属性
为了给 Vue 一个提示,以便它能跟踪每个节点的身份,从而重用和重新排序现有元素,你需要为每项提供一个唯一 key 属性。理想的 key 值是每项都有的唯一 id。这个特殊的属性相当于 Vue 1.x 的 track-by ,但它的工作方式类似于一个属性,所以你需要用 v-bind 来绑定动态值 (在这里使用简写):
<div v-for="item in items" :key="item.id">
<!-- 内容 -->
</div>
2
3
注意:key 并不与 v-for 特别关联,建议尽可能在使用 v-for 时提供 key,除非遍历输出的 DOM 内容非常简单,或者是刻意依赖默认行为以获取性能上的提升。
# 数组更新检测
一些操作数组的方法,编译会检测,从而会促使视图更新。
# 变异方法
push()pop()shift()unshift()splice()sort()reverse()
上面这些数组操作方法,会直接改变原始数组称为变异方法,会促使视图自动更新。
# 替换数组
学了 JavaScript 标准对象库,都知道有些数组方法是不直接改变原数组的,这里称他们为非变异方法,例如:filter()、slice()、concat(),他们都是返回一个新数组,那么,在 Vue 中使用到这些方法,怎么样才能促使视图更新呢?我们就必须使用数组替换法,将非变异方法返回的新数组直接赋值给的旧数组
this.nav = this.nav.slice(1, 4);
# 注意
由于 JavaScript 的限制,Vue 不能检测以下变动的数组:
- 当你利用索引直接设置一个项时,例如:
vm.items[indexOfItem] = newValue - 当你修改数组的长度时,例如:
vm.items.length = newLength
例子:
var app = new Vue({
data: {
items: ["a", "b", "c"],
},
});
app.items[1] = "x"; // 不是响应性的
app.items.length = 2; // 不是响应性的
2
3
4
5
6
7
上去直接这样改值操作是没有问题的,但是不是响应式的,并不能触发视图更新,需要用其他方法代替。
例如这样的操作 app.items[indexOfItem] = newValue ,可以用以下两种代替。
// Vue.set
Vue.set(vm.items, indexOfItem, newValue);
// Array.prototype.splice
vm.items.splice(indexOfItem, 1, newValue);
2
3
4
# 显示过滤
显示一个数组的过滤或排序副本,而不实际改变或重置原始数据。在这种情况下,可以创建返回过滤或排序数组的计算属性。
例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<span v-for="number in oddNumber">{{number}}</span>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
numberArray: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],
},
computed: {
//计算 numberArray 中为奇数的 oddNumber 奇数数组
oddNumber: function () {
return this.numberArray.filter(function (number) {
return number % 2 === 1;
});
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
运行结果:
如果你不想用计算属性,你也可以直接使用 方法 去操作,例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- v-for 内直接调用方法 -->
<span v-for="number in getOddNumber()">{{number}}</span>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
numberArray: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],
},
methods: {
//定一个一个获取数组内奇数的方法 filter 数组对象的过滤方法
getOddNumber: function () {
return this.numberArray.filter(function (number) {
return number % 2 === 1;
});
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
运行结果:
# v-for 循环一段值
在开发中我们会遇到要需要一段值的情况,不管是字符拼接,还是分页,我们都要用到,在 Vue 中我们可以用 v-for 轻松实现。
循环出 10 页分页:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- :style 绑定样式 -->
<span v-for="number in 10" :style="styleObject">{{number}}</span>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
//指定分页样式
styleObject: {
fontSize: "14px",
color: "#fff",
background: "green",
padding: "5px 10px",
border: "1px solid #fff",
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
运行结果:
# v-for 与 v-if 搭配使用
循环中嵌套控制,开发中很常见,在 Vue 中我们也可以这样使用。
例子,数组有元素就循环渲染,没有就渲染提示信息:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-if="numbers.length">
<div v-for="item in numbers">{{item}}</div>
</div>
<div style="color:red" v-else>请添加数组元素</div>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
numbers: [1, 2, 3, 4],
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
数组内有元素:
数组内没有元素 numbers:[]:
# 综合小练习,多级炫酷菜单渲染
该练习综合了数组渲染、对象渲染,v-if 、v-show、 key 、事件方法等知识
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>syl-vue-test</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
}
ul {
list-style: none;
}
nav,
ul {
width: 100%;
display: flex; /* 开启弹性盒模型 布局方式*/
flex-direction: row;
justify-content: center;
background: yellowgreen;
}
nav > ul > li {
width: 20%;
height: 100%;
text-align: center;
line-height: 50px;
}
nav > ul > li:hover {
box-shadow: 1px 0px 10px #fff;
}
nav > ul > li > ul {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
nav > ul > li > ul > li {
box-shadow: 1px 0px 10px #fff;
}
nav > ul > li > a {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
</style>
<!-- 引入 vue.js -->
<script src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1262/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<nav>
<ul>
<!-- 循环渲染一级菜单 -->
<!-- 鼠标移入触发currentIndex(index)函数,更正current是当前菜单的index, 鼠标移出重置current为空 事件回调方法在methods中实现-->
<li
v-for="(nav,index) in navbar"
:key="index"
@mouseover="currentIndex(index)"
@mouseout="changeIndex"
>
<!-- nav.name 一级菜单名字 -->
<a href="javascript:;">{{nav.name}}</a>
<!-- 如果nav.child存在,说明有子菜单,再次循环渲染子菜单 -->
<!-- 子菜单v-show 如果当前菜单的 index 等于 鼠标移入那个菜单的下标我们就展示出子菜单-->
<ul v-if="nav.child" v-show="current===index">
<li v-for="item in nav.child">
<a href="javascript:;">{{item}}</a>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
//navbar 模拟后台获取到的菜单列表
navbar: [
{
name: "home",
child: ["homeItem", "homeItem"],
},
{
name: "contact",
child: ["contactItem", "contactItem"],
},
{
name: "about",
},
],
//current 当前鼠标在那个菜单上 ,初始时没有值
current: null,
},
methods: {
//更正 当前鼠标移入的是哪个菜单的 index
currentIndex: function (index) {
this.current = index;
},
//鼠标移出 重置current 值
changeIndex: function () {
this.current = null;
},
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
虽然上面项目用 v-show 去实现子菜单,显得很累赘(css hover 轻松解决),重在传递的是一种思想,运行结果:

← class与style绑定 事件处理 →